1) What is HTML5?
Answer: HTML5 is the latest version of the HyperText Markup Language that can be referred to the WWW (World Wide Web) primary language, this markup language enhances a text file with bits of code, and this code which we can say as “markup” describes the structure of the document.
HTML5 provides some standard features like of CSS, HTML, JavaScript, and DOM, which in turn will reduce the requirement of external plugins. It’s more markup to replace scripting, better error handling, etc. HTML5 is device-independent.
2) What is <!DOCTYPE>? What are the different types of <!DOCTYPE> that are available?
Answer: The <!DOCTYPE> declaration provides instruction to the web browser to understand what information it should be display, and the need to start with <!DOCTYPE> declaration. In HTML5, DOCTYPE declaration is very short, and case-insensitive, and <!DOCTYPE html> is written at the top of every HTML5 page.
3) What are some of the key new features in HTML5?
Answer: Key new features of HTML5 include:
- Improved support for embedding graphics, audio, and video content via the new
<canvas>,<audio>, and<video>tags. - Extensions to the JavaScript API such as geolocation and drag-and-drop as well for storage and caching.
- Introduction of “web workers”.
- Several new semantic tags were also added to complement the structural logic of modern web applications. These include the
<main>,<nav>,<article>,<section>,<header>,<footer>, and<aside>tags. - New form controls, such as
<calendar>,<date>,<time>,<email>,<url>, and<search>.
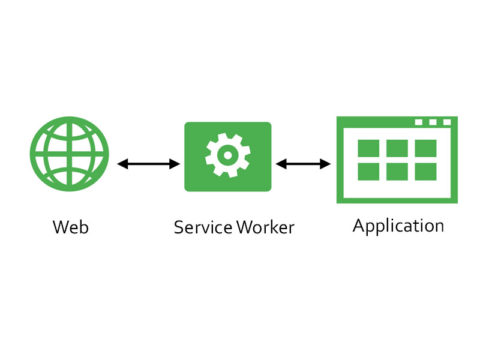
4) What are “web workers”?
Answer: Web workers at long last bring multi-threading to JavaScript.
A web worker is a script that runs in the background (i.e., in another thread) without the page needing to wait for it to complete. The user can continue to interact with the page while the web worker runs in the background. Workers utilize thread-like message passing to achieve parallelism.
5) Briefly describe the correct usage of the following HTML5 semantic elements: <header>, <article>, <section>, <footer>.
Answer:
- The
<header>element is used to contain introductory and navigational information about a section of the page. This can include the section heading, the author’s name, time and date of publication, table of contents, or other navigational information. - The
<article>element is meant to house a self-contained composition that can logically be independently recreated outside of the page without losing it’s meaining. Individual blog posts or news stories are good examples. - The
<section>element is a flexible container for holding content that shares a common informational theme or purpose. - The
<footer>element is used to hold information that should appear at the end of a section of content and contain additional information about the section. Author’s name, copyright information, and related links are typical examples of such content.
6) What is HTML5 Web Storage? Explain localStorage and sessionStorage.
Answer: With HTML5, web pages can store data locally within the user’s browser.
Earlier, this was done with cookies. However, Web Storage is more secure and faster. The data is not included with every server request, but used ONLY when asked for.
The data is stored in name/value pairs, and a web page can only access data stored by itself. Unlike cookies, the storage limit is far larger (at least 5MB) and information is never transferred to the server.
The difference between localStorage and sessionStorage involves the lifetime and scope of the storage.
Data stored through localStorage is permanent: it does not expire and remains stored on the user’s computer until a web app deletes it or the user asks the browser to delete it. SessionStorage has the same lifetime as the top-level window or browser tab in which the script that stored it is running. When the window or tab is permanently closed, any data stored through sessionStorage is deleted.
Both forms of storage are scoped to the document origin so that documents with different origins will never share the stored objects. But sessionStorage is also scoped on a per-window basis. If a user has two browser tabs displaying documents from the same origin, those two tabs have separate sessionStorage data: the scripts running in one tab cannot read or overwrite the data written by scripts in the other tab, even if both tabs are visiting exactly the same page and are running exactly the same scripts.
7) What is the difference between span and div?
Answer: The difference is that span gives the output with display: inline and div gives the output with display: block.
span is used when we need our elements to be shown in a line, one after the other.
8) What’s the difference between the <svg> and <canvas> elements?
Answer: The <svg> element is a container for SVG graphics. SVG has several methods for drawing paths, boxes, circles, text, and even bitmap images.
SVG is a language for describing 2D graphics, but <canvas> allows you to draw 2D graphics on the fly using JavaScript.
SVG is XML-based, which means that every element is available within the SVG DOM. You can attach JavaScript event handlers for an element.
In SVG, each drawn shape is remembered as an object. If attributes of an SVG object are changed, the browser can automatically re-render the shape.
Canvas is rendered pixel by pixel. In canvas, once the graphic is drawn, it is forgotten by the browser. If its position should be changed, the entire scene needs to be redrawn, including any objects that might have been covered by the graphic.
9) What are the New tags in Media Elements in HTML5?
Answer: The new tags in Media Elements in HTML5 are enlisted below:
- <audio>: Apply for multimedia contents like sounds, audio streams or music, embed audio content without the requirement of any additional plug-in like flash player.
- <video>: Apply for video content like video streams or movie clip, embed video content etc.
- <source>: Apply for multiple media resources in media elements, such as audio, video, picture etc.
- <embed>: Apply for an external application or embedded content (a plug-in).
- <track>: Apply for text tracks in the media elements such as video or audio. This tag is used for subtitles or caption files while the video media is playing.
10) Explain new Form input types in HTML5.
Answer: HTML5 has 14 new forms input types:
- Date: This is a Date picker, we can pick a date by using type = “date”.
- Week: This is a Week picker, we can pick a week by using type = “week”.
- Month: This is a Month picker, we can pick a month by using type = “month”.
- Time: This is a Time picker, we can pick the time by using type = “time”.
- Datetime: This is a combined date and time, we can pick the combination of date and time by using type = “datetime”.
- Datetime-local: A combined local date and time, we can pick the combination of local date and time using type = “DateTime-local”.
- Email: Allows one or more Email Addresses, we can enter multiple email addresses using type = “email”.
- Tel: Allows different phone numbers around the world. A phone number is validated by the client-side. We can enter a phone number using type = “tel”.
- Search: Allows to search queries by input text. We can enter multiple queries using type = “search”.
- Number: Allows inserting a numerical value with additional attributes such as min, max. etc., and we can enter multiple numerical values using type = “number”.
- Url: A url input type, that is used for the web address. In a single url, we can use multiple attributes using type = “url”.
- Color: Allows to select multiple colors, we can pic multiple color using type = “color”.
- Range: Allows to insert a numerical value within a specific range, Range is similar to the number but it is much specific. We can enter a numerical value within a range using type = “range”.
- Placeholder: Allows to display a short hint (usually in a light color) in the input fields, before we enter the value. We can write a short hint in the input field by using type = “placeholder”.
11) Are HTML tags case sensitive?
Answer: No!
12) What is the purpose of ‘figure’ tag in HTML5?
Answer: This tag can be used to associate a caption together with some embedded content, such as a graphic or video.
13) What is Web Forms 2.0?
Answer: Web Forms 2.0 is an extension to the forms features found in HTML4. Form elements and attributes in HTML5 provide a greater degree of semantic mark-up than HTML4 and remove a great deal of the need for tedious scripting and styling that was required in HTML4.
14) What is the purpose of ‘output’ tag in HTML5?
Answer: HTML5 introduced a new element <output> which is used to represent the result of different types of output, such as output written by a script.